accumulated earnings tax calculation example
The accumulated earnings tax is equal to 20 of the accumulated taxable income and is imposed in addition to other taxes required under the Internal Revenue Code. Instead they are retained to be reinvested in a new business opportunity to increase inventory levels to lower long-term debt or to increase cash reserves.
Prepared By Lilybeth A Ganer Revenue Officer Ppt Download
Corporations Subject to the 531 Tax IV.

. A 400000 distribution in year 6 will be sourced first from the current-year EP as shown in Exhibit 3. The threshold is 25000 without accumulated earning tax. RE Initial RE net income dividends.
The Accumulated Earnings Tax is more like a penalty since it is assessed by the IRS often years after the income tax. Rationale Imposition of Tax III. Accumulated earnings and profits EP is an accounting term applicable to stockholders of corporations.
The Accumulated Earnings Tax IRC. Retained Earnings 10 million 6 million 2 million 14 million. There is a certain level in which the number of earnings of C corporations can get.
Accumulated earnings and profits are less than the. The tax is in addition to the regular corporate income tax and is assessed by the IRS typically during an IRS audit. If the corporation was required to complete Schedule M-1 Form 1120 or Schedule M-3 Form 1120 for the tax year also attach.
On a personal level the accumulated. There is no IRS form for reporting the AET. In this guide well be explaining its importance how to calculate it and.
Accumulated Deficit Example Calculation. The accumulated earnings tax also called the accumulated profits tax is a tax on abnormally high levels of earnings retained by a company. The base for the accumulated earnings penalty is accumulated taxable income.
They are the amount of profit the company has reinvested in the business since its inception. This is because the accumulated earnings tax is directed at regular corporations who hold an excess of retained earnings instead of being distributed as dividends to shareholders. The accumulated earnings tax is a 20 penalty that is imposed when a corporation retains earnings beyond the.
The rate for the accumulated earnings tax is the same as the rate individual taxpayers pay on dividends or 20. Breaking Down Accumulated Earnings Tax. Accumulated earnings somewhat reflect a companys dividend policy because it reflects a companys.
The company made 700000 in net profits and paid dividends worth 300000 in the same year. Rather accumulated earnings demonstrate what a company did with its profits. The accumulated earnings credit allowable under section 535 c 1 on the basis of the reasonable needs of the business is determined to be only 20000.
The accumulated earnings tax may be imposed on a corporation for a tax year if it is determined that the corporation has attempted. When the revenues or profits are above this level the firm will be subjected to accumulated earnings tax if they do not distribute the dividends to shareholders. Therefore the 65 of taxable income limit does not apply.
REASONABLE NEEDS OF THE BUSINESS. The tax rate on accumulated earnings is 20 the maximum rate at which they would be taxed if distributed. Accumulated Earnings Tax.
The Worksheets also contain an illustration of how a corporation could analyze its exposure to the accumulated earnings tax and a sample taxpayers statement pursuant to 534c and Regs. Of the 400000 distribution the current-year EP will cover the first 117000. Up to 10 cash back 21.
The retained earnings will be 100000 700000 - 300000 500000 This figure is recorded in. If a corporation pursues an earnings accumulation strategy where the accumulation is to avoid the tax on dividends rather than having a business purpose then IRC 532 provides an accumulated earnings tax that can be assessed on accumulated earnings with no clear business purpose. These reinvestments are either asset purchases or liability reductions.
Its taxable income is 25000 100000 75000 before the deduction for dividends received. Publicly held corporations with many. The parties disagreed on the correct tax computation and instituted the current case to determine the right amount.
The value is part of a businesss balance sheet - more specifically its listed under the shareholders equity division. In a financially stable company if a company with a retained earnings balance of 10 million just generated 6 million in net income and paid 2 million in dividends the retained earnings for the current period is 14 million. However since the amount by which 150000 exceeds the accumulated earnings and profits at the close of the preceding taxable year is more than 20000 the minimum accumulated earnings.
This tax evolved as shareholders began electing to have companies retain earnings rather than pay them out as dividends in an effort to avoid. A computation of earnings and profits for the tax year see the example of a filled-in worksheet and a blank worksheet below. Section 531 for being profitable and not paying a sufficient level of dividends.
Adjustments to this calculation or other methods may be appropriate. The remaining 283000 distribution amount will be absorbed by the accumulated EP balance of. Corporation has a book net income of 20 million 500000 of book depreciation 1 million of tax depreciation 500000 of earnings and profits depreciation 25 million interest paid but not deducted for federal income tax purposes 15 million of federal income taxes paid and 3 million of meals and.
If imposed the earnings are subject to triple taxation when eventually. X has been a profitable. Next a corporation should determine how it will use any earnings accumulated in excess of its working capital needs.
The accumulated earnings of a firm are profits generated but not distributed to the shareholders as cash dividends or as corporate profit taxes. Accumulated earnings and profits are a companys net profits after paying dividends to the. It is presumed that a corporation can retain up to 25000000 or 15000000 for certain service corporations for.
For example lets assume a certain company has 100000 in accumulated earnings at the beginning of the year. If it claims the full dividends-received deduction of 65000 100000 65 and combines it with an operations loss of 75000 it will have an NOL of 40000. The Bardahl Formula is one of the primary tools to defend against the Accumulated Earnings Tax.
Suppose that a US. Accumulated profit also known as retained earnings is the cash that remains after companies distribute dividends to their shareholders. It compensates for taxes which cannot be levied on dividends.
It required the parties to compute the new tax liability based on the corporations holdings under the courts rule 155.
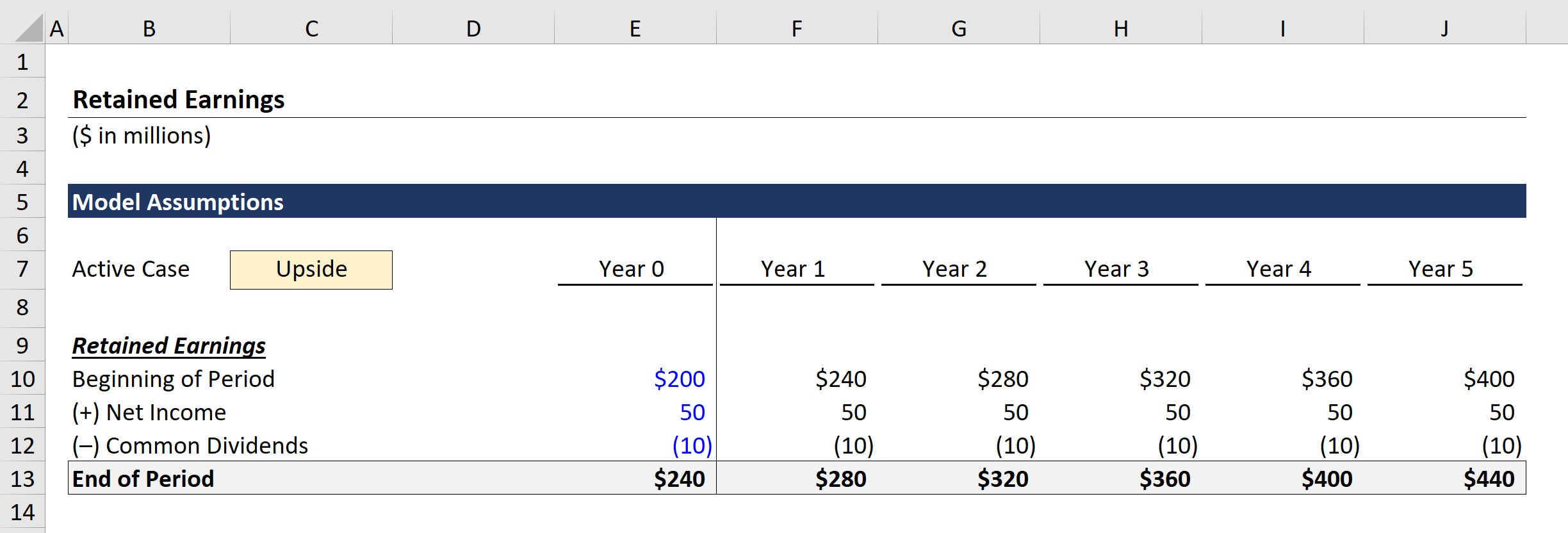
Retained Earnings Formula And Excel Calculator

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part I

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part Ii

What Are Retained Earnings Bdc Ca

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study
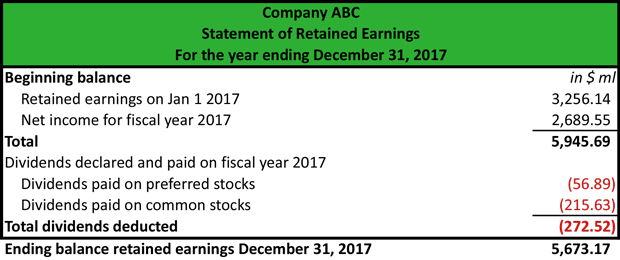
What Are Accumulated Earnings Definition Meaning Example

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

What Are Earnings After Tax Bdc Ca

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study

Determining The Taxability Of S Corporation Distributions Part Ii

Retained Earnings Formula Daily Business
What Are Accumulated Earnings Profits Accounting Clarified

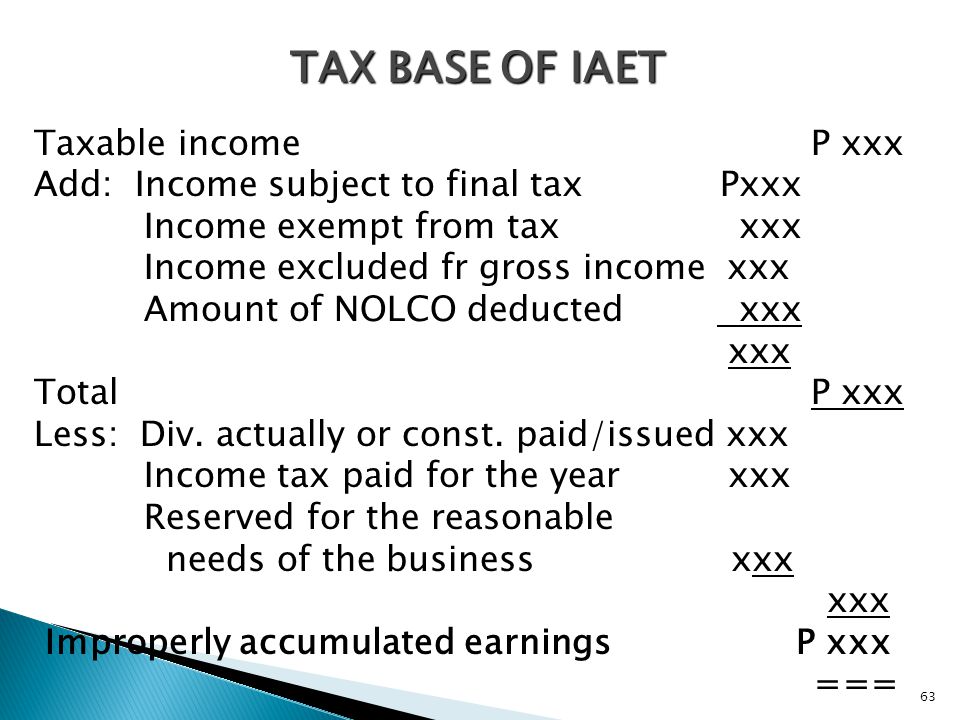
Income Tax Computation Corporate Taxpayer 1 2 What Is A Corporation Corporation Is An Artificial Being Created By Law Having The Rights Of Succession Ppt Download

Income Tax Computation Corporate Taxpayer 1 2 What Is A Corporation Corporation Is An Artificial Being Created By Law Having The Rights Of Succession Ppt Download

